We use cookies to personalise site content, social media features and to analyse our traffic. We also share information about your use of this site with our advertising and social media partners.
Posted by - tejask kam -
on - Sep 5 -
Filed in - Other -
45 Views - 0 Comments - 0 Likes - 0 Reviews
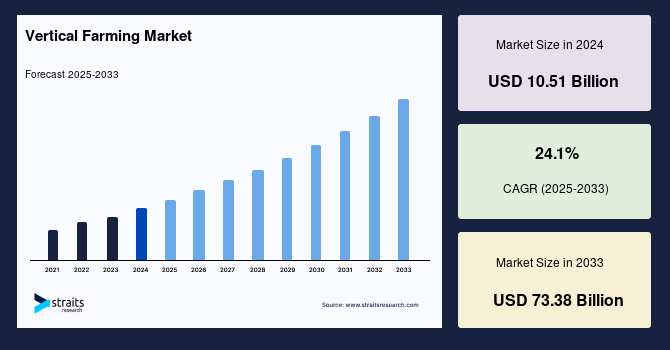
The global vertical farming market is undergoing exponential growth and transformation, driven by the urgent need for sustainable agricultural practices, urban food security, and technological advancements.
The global vertical farming market size was valued at USD 10.51 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 13.04 billion in 2025 to reach USD 73.38 billion by 2033,exhibiting a CAGR of 24.1% during the forecast period (2025-2033).
Vertical farming is an innovative agricultural method that involves growing crops vertically in stacked layers, shelves, or towers often indoors under controlled conditions such as artificial lighting and regulated temperature. Unlike traditional horizontal farming, vertical farming aims to optimize space utilization by increasing productivity within smaller land footprints. These indoor farms predominantly employ technologies like LED lighting, sensors, robotics, and sophisticated software algorithms to precisely control growth parameters such as light exposure, humidity, and temperature.
Three key cultivation techniques are commonly associated with vertical farming: hydroponics (growing plants without soil using nutrient-rich water), aeroponics (roots suspended in air misted with nutrients), and aquaponics (a synergistic system combining hydroponics with fish farming). Together, they enable resource-efficient production with faster crop cycles and more predictable yields.
Several global factors have accelerated the adoption of vertical farming:
Limited Arable Land and Urbanization: With agricultural land shrinking due to urban sprawl, deforestation, and erosion, vertical farming offers a solution to meet growing food demands efficiently within urban centers. It allows for local production, shortening supply chains and reducing transportation-related emissions and costs.
Climate Change Resistance: Vertical farming is inherently resilient to variable weather conditions, allowing year-round crop production irrespective of seasonal and climate disruptions, which increasingly threaten conventional agriculture.
Technological Advancements: Innovations in LED lighting technology have been pivotal. LEDs provide energy-efficient, customizable light spectrums that optimize photosynthesis. Integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics provide real-time monitoring and automated adjustments to grow conditions, enhancing productivity and reducing resource waste.
Growing Demand for Fresh and Organic Produce: Consumer preference has shifted strongly toward pesticide-free, locally grown, nutritious food. Vertical farms can deliver high-quality, fresh greens, herbs, and vegetables closer to consumers with minimal chemical inputs.
Hydroponics dominates the vertical farming segment due to its simplicity, scalability, and efficient nutrient delivery. Plants grow in water infused with essential macro- and micronutrients directly accessible to roots, accelerating growth rates. Aquaponics similarly thrives by coupling fish cultivation with plant growth, where fish waste serves as a natural fertilizer in a symbiotic system, reducing external nutrient expenses.
Lighting remains a critical component, with LED technology holding the largest share and expected to grow at approximately 26.4%. Adjustable spectrum LEDs enable growers to tailor light quality, duration, and intensity to specific crops, enhancing photosynthetic efficiency and crop quality while lowering electricity consumption compared to traditional high-pressure sodium lamps.
Sensors and environmental control systems facilitate precision agriculture by continuously collecting data on parameters such as temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, pH, and moisture. These advanced systems empower farmers to optimize growth environments, maximize yields, and manage resources responsibly.
North America leads the global market, driven by significant investments in sustainable agriculture solutions, supportive government policies, and a rapidly expanding urban farming ecosystem. Technological innovation hubs and established companies in the U.S. and Canada, such as AeroFarms and American Hydroponics, contribute to market leadership.
Europe is the fastest-growing market, with a CAGR close to 26.7%, fueled by rising consumer demand for local, organic produce and reducing environmental footprints. Countries like the U.K., Germany, and the Netherlands are at the forefront of adopting vertical farming initiatives, supported by nonprofit organizations and increased startup activity.
Asia-Pacific, particularly India, China, and Japan, represents an enormous market due to the high population density, limited arable land, and progressive adoption of modern agriculture techniques. Rapid urbanization and the need to ensure food security drive interest in vertical farming systems.
Emerging markets in the Middle East and Africa are also beginning to explore vertical farming to counteract harsh climatic conditions and food supply challenges, thereby opening new growth avenues.
Vertical farming boasts a range of impressive advantages over conventional farming:
Space Efficiency: Some vertical farms produce over 350 times more crops per square yard than traditional farms due to vertical stacking and optimized resource usage.
Resource Conservation: Water use is up to 90% less than in field farming due to recirculating nutrient systems. Controlled environments prevent fertilizer runoff and pesticide contamination.
Year-Round Production: Independent of seasonal changes, vertical farms ensure a continuous supply of fresh produce.
Urban Food Security: Vertical farms situated in or near cities dramatically reduce transportation costs, spoilage, and carbon footprint, enhancing local access to fresh food.
Despite its potential, vertical farming faces challenges. High initial capital investments are necessary to establish facilities equipped with advanced lighting, climate control, and growing infrastructure. Operational costs, particularly energy consumption for lighting and climate regulation, can be substantial, although continuously declining LED costs and renewable energy integration mitigate these pressures.
Labor expertise and dependence on sophisticated technology require ongoing training and maintenance. Moreover, pollination and crop variety limitations may restrict certain agricultural applications.
Nevertheless, the market outlook remains highly optimistic. Technological progress in AI-driven farm management, renewable energy integration, and automated robotics will further reduce costs and improve efficiency. As consumer demand for sustainable, fresh, and organic food intensifies globally, vertical farming is positioned to become a cornerstone of future food systems.
In conclusion, vertical farming represents a transformative approach to agriculture that addresses many pressing global challenges land scarcity, climate volatility, food security, and sustainability. By combining cutting-edge technology with innovative cultivation methods, it holds the promise of revolutionizing how food is produced and consumed, ensuring a greener and more resilient agricultural future worldwide.

“To assist disaster survivors by providing a source for them to come together in time of need, to aid in the listing of events, information and other forms of assistance, and continuing support through the recovery process.”
Share this page with your family and friends.